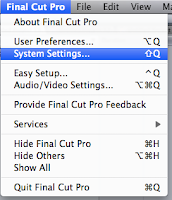
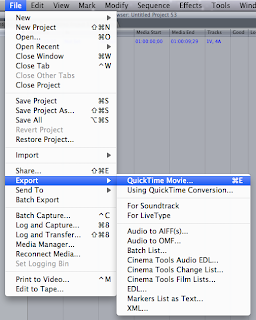
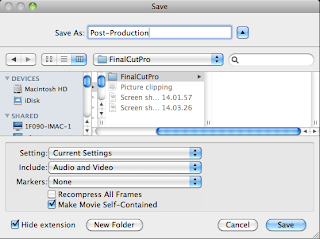
program is transmitted over the cable directly to the receiver TV.
Cable was created in 1947 by John Walson and was originally called
CATV (Community Antenna Television). Two advantages to cable
are, it has a better reception and has a better picture and sound. A
disadvantage is that cable isn't available in as many places as satellite.
 Satellite is another way to broadcast programs. Satellite is a signal that is sent to satellites orbiting the earth and then amplifies the signal before sending it back down to earth. The first satellite television broadcast was in 1978 and was developed to direct to home receivers in 1980. Two advantages to satellite are, it is available in areas that cannot receive cable. And it provides a sharper image than off air broadcast. A disadvantage is that the weather can disrupt connection.
Satellite is another way to broadcast programs. Satellite is a signal that is sent to satellites orbiting the earth and then amplifies the signal before sending it back down to earth. The first satellite television broadcast was in 1978 and was developed to direct to home receivers in 1980. Two advantages to satellite are, it is available in areas that cannot receive cable. And it provides a sharper image than off air broadcast. A disadvantage is that the weather can disrupt connection.
 Freeview is a free digital broadcasting system. It receives digital terrestrial transmission and can be used with any TV. Freeview was launched in 2002, it was jointly operated by five shareholders, BBC, ITV, Channel 4, BSkyB and Arqiva. Two advantages of Freeview are, its free and safe. And provides a weeks listing of programs. A
Freeview is a free digital broadcasting system. It receives digital terrestrial transmission and can be used with any TV. Freeview was launched in 2002, it was jointly operated by five shareholders, BBC, ITV, Channel 4, BSkyB and Arqiva. Two advantages of Freeview are, its free and safe. And provides a weeks listing of programs. A
 Internet TV is a digital download of programs via the internet. Internet TV became very popular in the UK through BBC iPlayer, 4oD, ITV Player and Demand Five. Two advantages to internet TV are, its available everywhere that there is an internet connection. It has old shows available that aren't on TV anymore. A disadvantage is, they often include adverts.
Internet TV is a digital download of programs via the internet. Internet TV became very popular in the UK through BBC iPlayer, 4oD, ITV Player and Demand Five. Two advantages to internet TV are, its available everywhere that there is an internet connection. It has old shows available that aren't on TV anymore. A disadvantage is, they often include adverts.
 Satellite is another way to broadcast programs. Satellite is a signal that is sent to satellites orbiting the earth and then amplifies the signal before sending it back down to earth. The first satellite television broadcast was in 1978 and was developed to direct to home receivers in 1980. Two advantages to satellite are, it is available in areas that cannot receive cable. And it provides a sharper image than off air broadcast. A disadvantage is that the weather can disrupt connection.
Satellite is another way to broadcast programs. Satellite is a signal that is sent to satellites orbiting the earth and then amplifies the signal before sending it back down to earth. The first satellite television broadcast was in 1978 and was developed to direct to home receivers in 1980. Two advantages to satellite are, it is available in areas that cannot receive cable. And it provides a sharper image than off air broadcast. A disadvantage is that the weather can disrupt connection. Freeview is a free digital broadcasting system. It receives digital terrestrial transmission and can be used with any TV. Freeview was launched in 2002, it was jointly operated by five shareholders, BBC, ITV, Channel 4, BSkyB and Arqiva. Two advantages of Freeview are, its free and safe. And provides a weeks listing of programs. A
Freeview is a free digital broadcasting system. It receives digital terrestrial transmission and can be used with any TV. Freeview was launched in 2002, it was jointly operated by five shareholders, BBC, ITV, Channel 4, BSkyB and Arqiva. Two advantages of Freeview are, its free and safe. And provides a weeks listing of programs. A
disadvantage is that it not available everywhere in the UK.
 Internet TV is a digital download of programs via the internet. Internet TV became very popular in the UK through BBC iPlayer, 4oD, ITV Player and Demand Five. Two advantages to internet TV are, its available everywhere that there is an internet connection. It has old shows available that aren't on TV anymore. A disadvantage is, they often include adverts.
Internet TV is a digital download of programs via the internet. Internet TV became very popular in the UK through BBC iPlayer, 4oD, ITV Player and Demand Five. Two advantages to internet TV are, its available everywhere that there is an internet connection. It has old shows available that aren't on TV anymore. A disadvantage is, they often include adverts.